Part 1 Basics of Ergonomic Seating
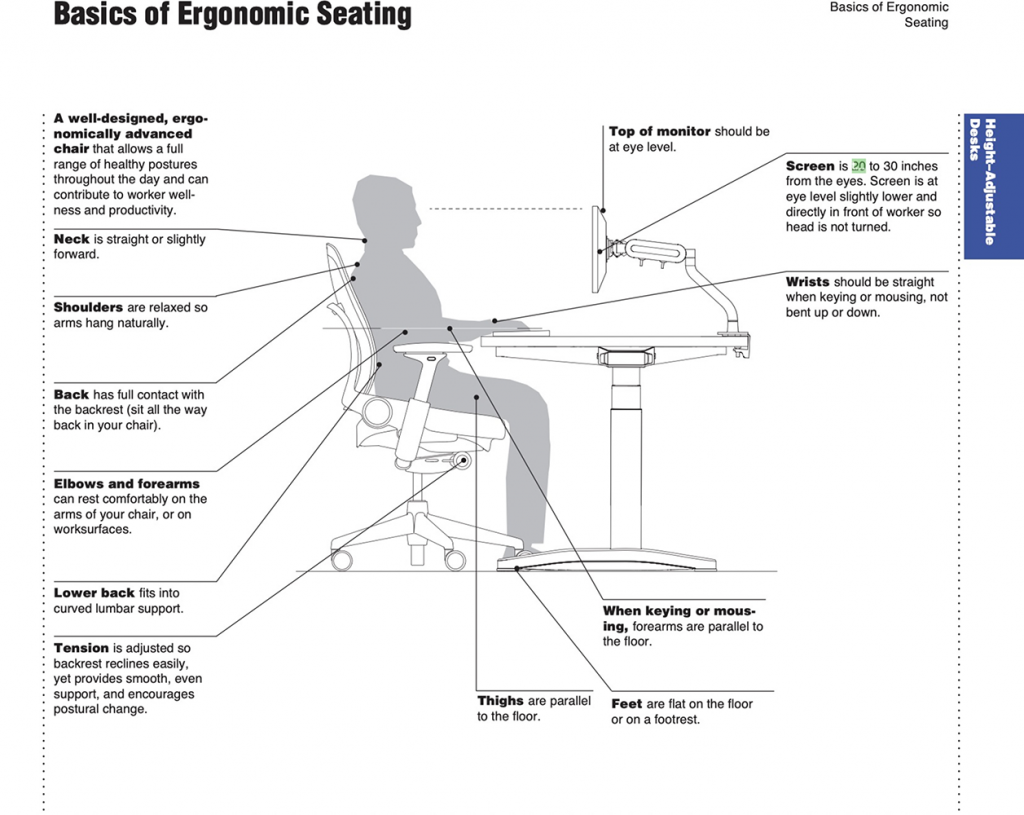
A chair that is ergo-nomically designed could allow a full range of healthy postures all through the day and benefits workers’ wellness and productivity.
——Neck: should be straight or slightly forward.
——Shoulders: Relax shoulders and let arms drop naturally;
——Back: Full contact between the backrest and the back;
——Elbows and Forearms: Can be placed comfortably on the arm of the chair or on the working surface.
——Lower back: Suits into the curved waist support.
——Tension: Adjustment makes back tilt easily, but provides smooth, even support and encourages changed postures.
——Top of monitor: Should be at eye level.
——Screen: Should be 20 to 30 inches from the eyes. The screen is slightly lower at the eye level, directly in front of the worker so the head does not need to turn.
——Wrist: When keying or mousing, wrists should be straight and do not bend up or down.
——When keying or mousing: Forearm is parallel to the ground.
——Feet: Should be flat on the foot pads.
——Thighs: Should be parallel to the ground.
Part 2 Basics of Standing and Monitor Arm Positioning For Desk
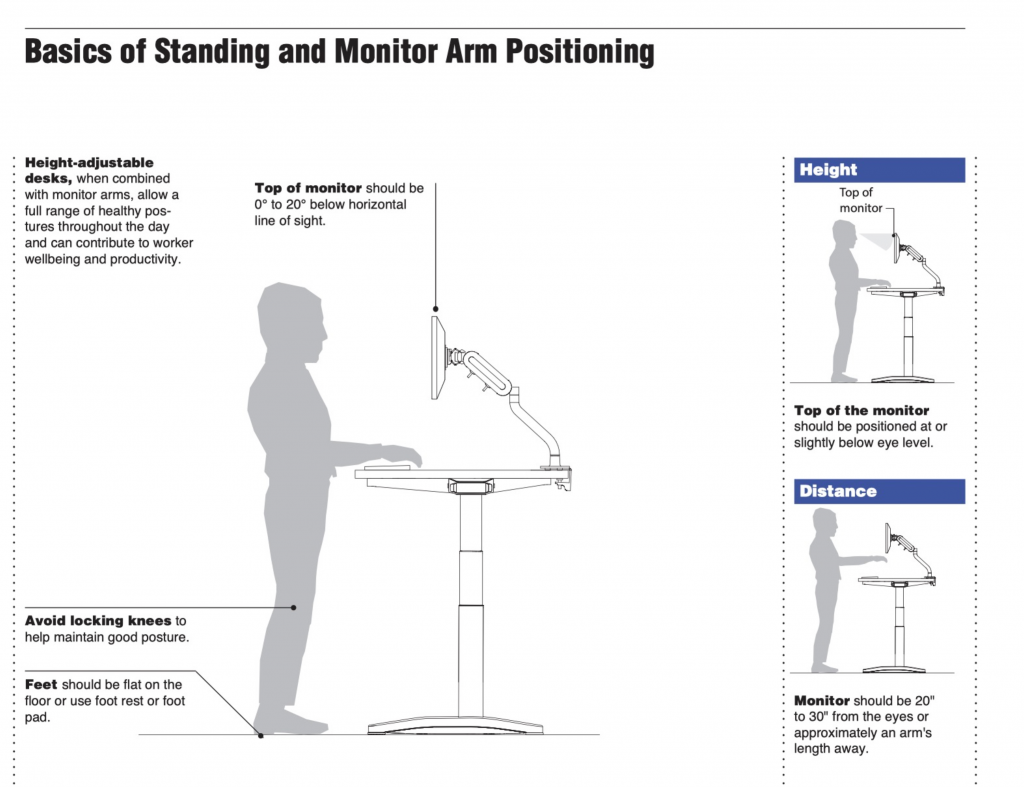
——Height adjustable desks: When used in conjunction with the monitoring arm, it could allow a full range of healthy postures all through the day and benefits workers’ wellness and productivity.
——The top of the display should be below the horizontal line of sight from 0 to20degrees.
——Avoid locking your knees to help maintain good posture.
——Feet should be placed flat on the foot restor or use the foot or foot rest
Height
Top of Monitor: Should be at or slightly below the eye level.
Distance
Monitor: Should be 20″ to 30″ from the eyes or about an arm’s length away.
Part 3 Basics of Standing and Monitor Arm Positioning for Desk